Unveiling the Secrets of the Client
Hello
JA4 fingerprinting focuses on
analyzing the
TLS Client Hello packet, which is sent unencrypted from
the client to the server at the start of a TLS connection.
This packet contains a treasure trove of information that can
uniquely identify the client application or its underlying
TLS library. Some of the key elements extracted by JA4
include:
- TLS
Version: The version of TLS supported by the
client.
- Cipher
Suites: The list of cryptographic algorithms the client can
use.
- TLS
Extensions: Additional features and capabilities supported
by the client.
- ALPN
(Application-Layer Protocol Negotiation): The
application-level protocol, such as HTTP/2 or HTTP/3, that
the client wants to use after the TLS
handshake.
JA4 in Action: Pivoting and Hunting on
VirusTotal
VirusTotal has integrated JA4
fingerprinting into its platform through the behavior_network
file
search modifier. This allows analysts to quickly
discover relationships between files based on their JA4
fingerprints.
To find the JA4 value, navigate to the “behavior” section of
the desired sample and locate the TLS subsection. In addition
to JA4, you might also find JA3 or JA3S there.
Example Search: Let’s say you’ve encountered a suspicious
file that exhibits the JA4 fingerprint
“t10d070600_c50f5591e341_1a3805c3aa63” during VirusTotal’s
behavioral analysis.
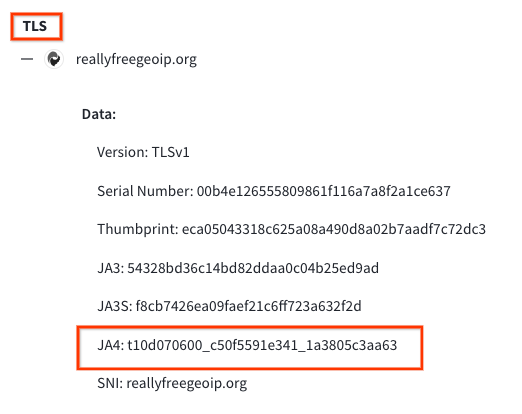
You can click on this JA4 to pivot using the
search query
behavior_network:t10d070600_c50f5591e341_1a3805c3aa63
finding other files with the same fingerprint This search
will pivot you to additional samples that share the same JA4
fingerprint, suggesting they might be related. This could
indicate that these files are part of the same malware family
or share a common developer or simply share a common TLS
library.

Wildcard Searches
To broaden your search, you can
use wildcards within the JA4 hash. For instance, the search:
behaviour_network:t13d190900_*_97f8aa674fd9
Returns files that match the
JA4_A and JA4_C components of the JA4 hash while allowing
for variations in the middle section, which often corresponds
to the cipher suite. This technique is useful for identifying
files that might use different ciphers but share other JA4
characteristics.
YARA Hunting Rules: Automating JA4-Based
Detection
YARA hunting rules using the
“vt” module can be written to
automatically detect files based on their JA4 fingerprints.
Here’s an example of a YARA rule that targets a specific JA4
fingerprint:
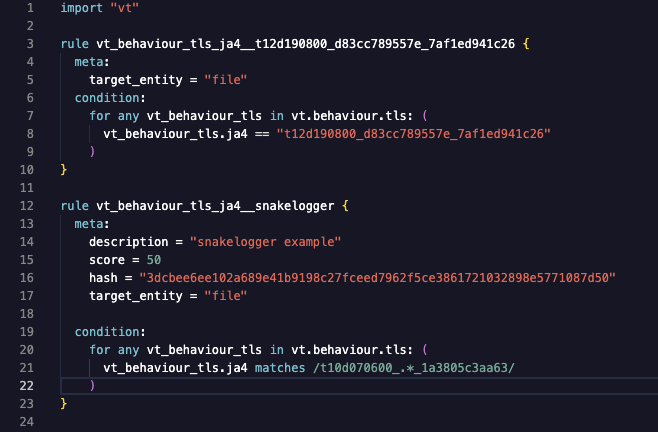
This rules will flag any file submitted to VirusTotal that
exhibits the matching JA4 fingerprint. The first example only
matches “t12d190800_d83cc789557e_7af1ed941c26” during
behavioral analysis. The second rule will match a regular
expression /t10d070600_.*_1a3805c3aa63/, only matching JA4_A
and JA4_C components, excluding the JA4_B cipher suite. These
fingerprints could be linked to known malware, a suspicious
application, or any TLS client behavior that is considered
risky by security analysts.
JA4: Elevating Threat
Hunting on VirusTotal
VirusTotal’s adoption
of JA4 client fingerprinting will provide users with an
invaluable tool for dissecting and tracking TLS client
behaviors, leading to enhanced threat hunting, pivoting, and
more robust malware identification.
Happy Hunting.

