The rise of .ai: cyber criminals (and Anguilla) look to profit
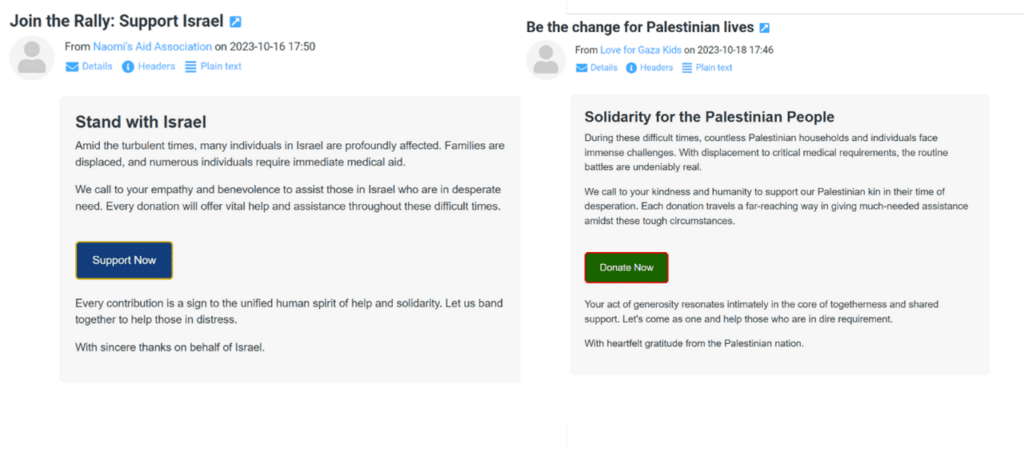
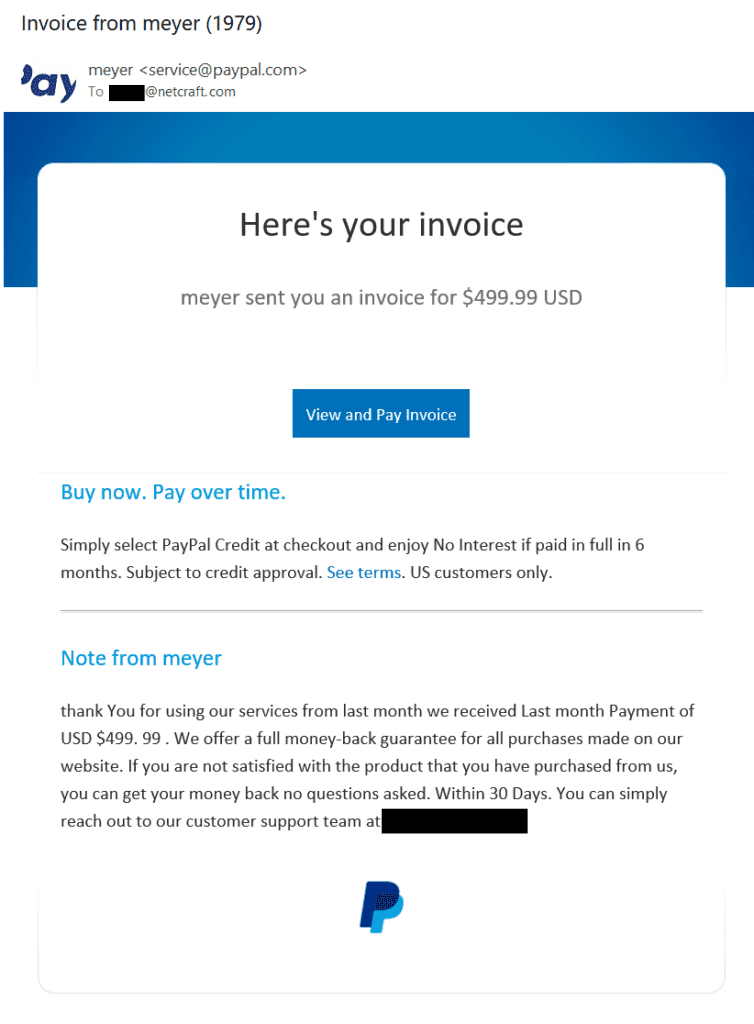
Given the global interest in artificial intelligence (AI), it comes as no surprise that cybercriminals are looking to exploit the media hype. 2023 has seen a rapid increase in AI-themed attacks, following the release of Large Language Model (LLM)-powered chatbot ChatGPT in late 2022 (which quickly became one of the fastest-growing consumer applications ever). One easy way to theme a website around AI is to use a domain name which highlights it, as a .ai domain does.
This blog takes a look at the popularity of the .ai domains in recent years and the malicious activity on them that Netcraft has detected and disrupted.
About the .ai TLD
.ai is the country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for the British Overseas Territory of Anguilla. Registrations for this ccTLD began in 1995, but these have accelerated rapidly due to the boom in AI and related industries. Related fees go to the treasury of the government of Anguilla who, according to a report in the New York Times, made $2.9 million in 2018 from .ai registrations.
The ccTLD is used by many legitimate businesses, including two of the biggest technology companies in the world. Google and Meta registered google.ai and facebook.ai in 2017, which redirect to websites promoting their work in the field of AI.
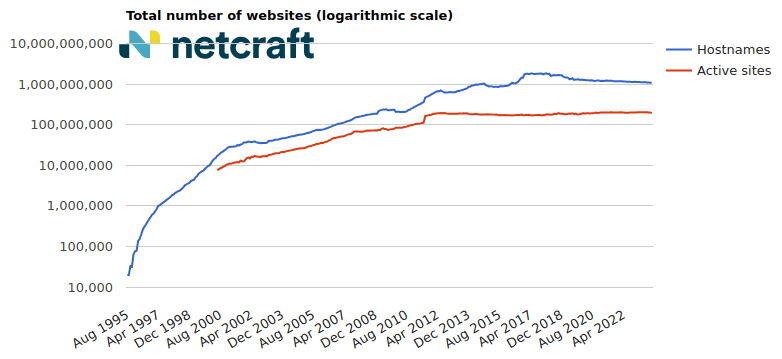
Since 2013, the number of .ai domains used by web servers has grown 12,523% from 913 to 115,245 domains. We can also see similar growth in IPs and Active sites, growing from 165 to 37,041 IPs and 647 to 112,600 Active Sites. We detected the first part of this massive growth in 2017, when the technology industry and the wider media first began to take notice of (and report on) the potential of AI.
However, we saw an even bigger explosion in …
Continue reading The rise of .ai: cyber criminals (and Anguilla) look to profit