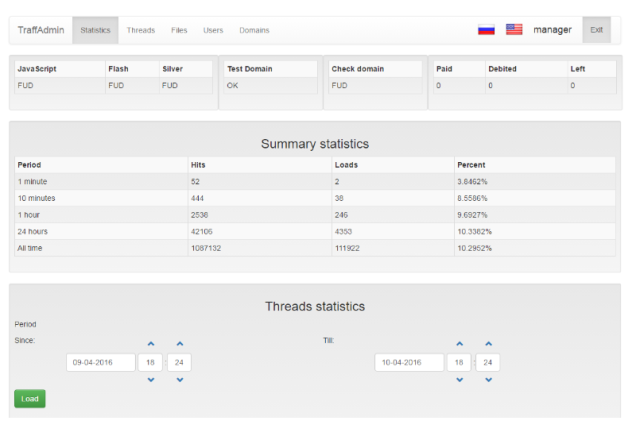
The Web console for Nuclear, the customer-friendly malware-as-a-service platform. Some Nuclear infrastructure operating on DigitalOcean servers was recently disrupted. (credit: Check Point)
Security researchers at Cisco Talos and Check Point have published reports detailing the inner workings of Nuclear, an “exploit kit” Web service that deployed malware onto victims’ computers through malicious websites. While a significant percentage of Nuclear’s infrastructure has been recently disrupted, the exploit kit is still operating—and looks to be a major contributor to the current crypto-ransomware epidemic.
Introduced in 2010, Nuclear has been used to target millions of victims worldwide, giving attackers the ability to tailor their attacks to specific locations and computer configurations. Though not as widely used as the well-known Angler exploit kit, it has been responsible for dropping Locky and other crypto-ransomware onto more than 140,000 computers in more than 200 countries, according to statistics collected by Check Point (PDF). The Locky campaign appeared to be placing the greatest demand on the Nuclear pay-to-exploit service.
Much of Talos’ data on Nuclear comes from tracking down the source of its traffic—a cluster of “10 to 15” IP addresses that were responsible for “practically all” of the exploit infrastructure. Those addresses were being hosted by a single cloud hosting provider—DigitalOcean. The hosting company’s security team confirmed the findings to Talos and took down the servers—sharing what was on them with security researchers.